Embarking on outdoor adventures immerses individuals in the beauty of nature, offering a sense of freedom and connection to the environment. However, amidst the serenity of the wilderness lies a critical consideration for survival: access to safe drinking water. Natural water sources, while picturesque and inviting, can conceal a host of invisible threats that jeopardize health and well-being. Bacteria, viruses, protozoa, heavy metals, and chemicals lurk in these pristine waters, posing significant health risks to individuals who consume untreated water.
In the face of these challenges, outdoor enthusiasts must arm themselves with knowledge and tools to ensure the safety of their hydration sources. Various water treatment methods have been developed to address the diverse array of contaminants found in wilderness water sources. Filtration, purification, and disinfection stand as pillars of defense against the harmful agents that can lurk in seemingly pure streams and lakes.
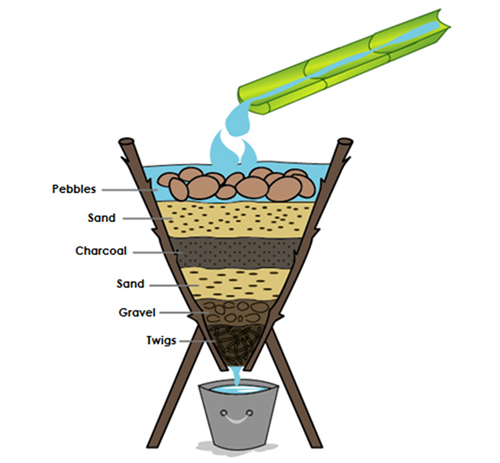
Filtration acts as the first line of defense, targeting visible impurities such as sediment, debris, and large particles that can affect water clarity and taste. While filtration can enhance the aesthetic qualities of water, it may not effectively remove microscopic threats like bacteria, viruses, protozoa, heavy metals, or chemicals. Understanding the limitations of filtration is crucial for outdoor enthusiasts to recognize when additional treatment methods are necessary to ensure water safety.
Purification methods take water treatment a step further by specifically targeting and neutralizing harmful microorganisms, chemicals, and heavy metals that may be present in natural water sources. Chemical treatments like iodine tablets and chlorine dioxide are effective in disinfecting water by killing bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, making it safe for consumption. Purification techniques offer a comprehensive approach to water treatment, addressing both visible and invisible contaminants to provide clean and potable water for outdoor enthusiasts.
Disinfection techniques focus on eradicating or inactivating microorganisms in water to prevent the transmission of waterborne diseases. Boiling water is a time-tested method of disinfection that effectively eliminates bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, ensuring the safety of drinking water in the wilderness. Chlorine-based disinfectants and ozone generators offer alternative means of disinfection, providing additional layers of protection against microbial contamination in emergency situations or when traditional treatment methods are unavailable.
In the realm of wilderness exploration, understanding the nuances of filtration, purification, and disinfection is paramount for selecting the most appropriate tools and techniques to safeguard hydration needs. By equipping themselves with knowledge and the right water treatment tools, outdoor enthusiasts can navigate the natural world with confidence, knowing that they have taken proactive steps to protect their health and vitality in the face of unseen threats lurking in the waters of the wild.
Filtration
Filtration stands as the frontline defense in the realm of wilderness water treatment, acting as the initial barrier against visible impurities that can compromise the quality of natural water sources. This method targets physical contaminants such as sediment, debris, and large particles, which can cloud the water and affect its taste and appearance. While filtration excels at enhancing water clarity and palatability, it is important to note that it may not be sufficient to eliminate microscopic threats like bacteria, viruses, protozoa, heavy metals, or chemicals that can lurk in untreated water sources.
In the wilderness, outdoor enthusiasts rely on a variety of tools and devices for filtration to ensure the safety of their drinking water. Portable water filters and water filter bottles are among the most popular choices, offering convenience and portability for on-the-go water treatment. These tools typically employ different filtration mechanisms, such as activated carbon, ceramic filters, or hollow fiber membranes, to physically strain out impurities and improve water quality.
One notable innovation in the realm of wilderness filtration is the Grayl purifier, a cutting-edge device that integrates advanced filtration technology to provide clean and safe drinking water in outdoor settings. The Grayl purifier utilizes a combination of activated carbon and ion exchange to target a broad spectrum of contaminants, including bacteria, protozoa, and certain chemicals. This dual filtration system effectively removes a wide range of impurities, ensuring that the water is not only clear and great-tasting but also safe for consumption.
By leveraging the capabilities of devices like the Grayl purifier, outdoor enthusiasts can enhance their water treatment efforts and enjoy peace of mind knowing that they are effectively removing harmful contaminants from their hydration sources. The integration of advanced filtration technologies in portable water filters empowers individuals to explore the wilderness with confidence, knowing that they have a reliable and efficient means of obtaining clean and potable water during their outdoor adventures.
Purification
Purification methods play a crucial role in wilderness water treatment by specifically targeting and neutralizing harmful microorganisms, chemicals, and heavy metals that may be present in natural water sources. These methods are designed to provide a comprehensive approach to water treatment, ensuring that the water is not only free from visible impurities but also safe for consumption by eliminating invisible threats that can pose health risks to individuals in the outdoors.
Chemical treatments are commonly employed for water purification in outdoor settings due to their effectiveness in disinfecting water and killing a wide range of microorganisms. Iodine tablets and chlorine dioxide are popular choices for wilderness purification, offering a convenient and portable solution for treating water on the go. Iodine tablets, for instance, work by releasing iodine into the water, which acts as a powerful disinfectant capable of killing bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, making the water safe for drinking.
While iodine tablets are lightweight and easy to carry, providing a practical solution for water purification in remote locations, it is important to note that they can impart a distinct taste to the water. The taste of iodine-treated water may be noticeable to some users, which can be a consideration for individuals who are sensitive to the flavor or odor of iodine. Despite this potential drawback, iodine tablets remain a popular choice for wilderness purification due to their effectiveness in disinfecting water and providing a reliable means of ensuring water safety in outdoor environments.
By understanding the capabilities and limitations of purification methods like chemical treatments, outdoor enthusiasts can make informed decisions when selecting water treatment options for their wilderness adventures. Choosing the right purification tools based on individual preferences and considerations, such as taste sensitivity, can enhance the overall water treatment experience and contribute to a safe and enjoyable outdoor journey.
Disinfection
Disinfection techniques play a vital role in wilderness water treatment by focusing on inactivating or eliminating microorganisms present in water sources to prevent the transmission of waterborne diseases. These methods are essential for ensuring the safety of drinking water in outdoor environments where natural water sources may be contaminated with harmful pathogens that can pose health risks to individuals.
Boiling water stands out as a reliable and time-tested method of disinfection that effectively kills bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, making the water safe for consumption. By bringing water to a rolling boil for a specified period, typically one minute or longer, the heat effectively destroys microbial contaminants, providing a simple yet effective means of purifying water in the wilderness. Boiling water is a widely recommended disinfection method due to its accessibility, ease of implementation, and proven efficacy in rendering water safe to drink.
In addition to boiling, chlorine-based disinfectants and ozone generators are alternative methods that can be used to treat water in the wilderness, offering an extra layer of protection against microbial contamination. Chlorine-based disinfectants, such as chlorine tablets or bleach, work by releasing chlorine into the water to kill bacteria and viruses, ensuring water safety for consumption. Ozone generators utilize ozone gas to disinfect water by destroying pathogens and organic contaminants, providing a chemical-free and environmentally friendly disinfection solution for outdoor enthusiasts.
These disinfection methods are particularly valuable in emergency situations or when other treatment options are unavailable, offering a reliable way to purify water and prevent the spread of waterborne illnesses in the wilderness. By incorporating disinfection techniques into their water treatment practices, outdoor adventurers can enhance their preparedness and resilience in challenging environments, ensuring that they have access to safe and potable water during their outdoor excursions.
In conclusion, the realm of wilderness water treatments offers a diverse array of methods tailored to address specific contaminants and ensure the purity of drinking water in outdoor environments. Each method, whether it be filtration, purification, or disinfection, plays a crucial role in safeguarding the health and well-being of individuals venturing into the wild, where water sources can harbor a multitude of unseen threats.
Filtration serves as the initial step in water treatment, focusing on physical impurities to enhance water clarity and taste. While filtration is effective at removing visible contaminants, it may not suffice in eliminating microscopic threats like bacteria, viruses, protozoa, heavy metals, or chemicals. In contrast, purification and disinfection methods delve deeper into water treatment by targeting harmful microorganisms, heavy metals, and chemicals to provide safe and potable water for consumption in the wilderness.
Choosing the right tools and techniques for water treatment is essential for maintaining hydration and health during outdoor adventures. Devices like Grayl purifiers, iodine tablets, and boiling water each offer unique benefits and considerations based on the contaminants present in the water source. By understanding the capabilities and limitations of these water treatment methods, outdoor enthusiasts can make informed decisions to protect their well-being while immersing themselves in the beauty of nature.
Chlorine
Chlorine-based disinfectants, such as chlorine tablets or bleach, are commonly used in outdoor environments to treat water and eliminate harmful microorganisms. Chlorine works by releasing chlorine ions into the water, effectively killing bacteria and viruses to make the water safe for consumption. Chlorine tablets are convenient and portable, making them a popular choice for wilderness water treatment. While chlorine can be highly effective in disinfecting water, it is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper dosing to ensure safe and effective treatment.
UV Lights (Steripen)
UV light sterilizers, such as the Steripen, offer a rapid and chemical-free method of disinfecting water in the wilderness. These devices use ultraviolet light to destroy the DNA of microorganisms, rendering them unable to reproduce and causing them to die off. The Steripen is compact, lightweight, and easy to use, making it a convenient tool for purifying water on backpacking trips or camping expeditions. UV light treatment is effective against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, providing a reliable solution for ensuring water safety in the outdoors.
Millbank Bag
The Millbank bag is a traditional water filtration device that is designed to remove sediment and debris from untreated water sources. Made of canvas or similar material, the Millbank bag is filled with water and allowed to drip through, trapping particles and impurities as the water passes through the fabric. While the Millbank bag is not a method of disinfection or purification, it serves as an effective tool for pre-filtering water before further treatment. This simple yet practical device can help improve water clarity and reduce the presence of visible contaminants in wilderness water sources.
Incorporating tools like chlorine, UV lights such as the Steripen, and the Millbank bag into wilderness water treatment practices expands the options available to outdoor enthusiasts for ensuring the safety and quality of their drinking water. Each tool offers unique benefits and considerations, allowing individuals to tailor their water treatment approach based on the specific contaminants present in the water source and their preferences for treatment methods. By leveraging a combination of tools and techniques, outdoor adventurers can enhance their preparedness and resilience in the face of waterborne risks, enabling them to stay hydrated and healthy while exploring the wonders of the natural world.
Ultimately, the ability to navigate the complexities of wilderness water treatment empowers individuals to venture into the outdoors with confidence, knowing that they have the knowledge and tools to ensure the safety of their hydration sources. By embracing a proactive approach to water treatment and staying informed about the best practices for wilderness hydration, outdoor adventurers can embark on their journeys with peace of mind, ready to explore and connect with the natural world while prioritizing their health and vitality.
In the realm of wilderness water treatment, a variety of tools and methods are available to outdoor enthusiasts to ensure the safety and purity of their drinking water. In addition to the previously discussed filtration, purification, and disinfection techniques, tools such as chlorine, UV lights like Steripen, and the Millbank bag offer unique approaches to water treatment in outdoor settings.