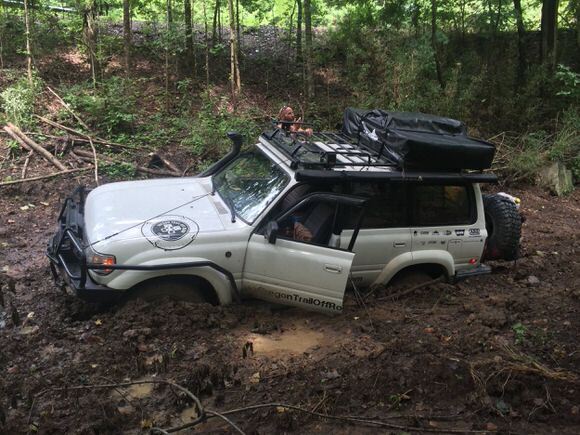
Here are the top 10 mistakes people make when overlanding in remote areas, especially without cellular coverage.
1. Lack of Navigation Skills
Overreliance on GPS Navigation
Technology Dependency
- Relying solely on GPS navigation systems can lead to a false sense of security, especially in areas where satellite signals may be weak or unavailable.
- GPS devices can malfunction, run out of battery, or lose signal in rugged terrain, leaving travelers disoriented and lost.
Limited Data Accuracy
- GPS maps may not always provide up-to-date information on road closures, trail conditions, or alternative routes, leading to potential navigation errors.
- Inaccurate mapping data can result in travelers taking wrong turns or getting stuck in challenging terrain.
Importance of Backup Navigation Methods
Traditional Navigation Tools
- Carrying physical maps, compasses, and guidebooks as backup navigation tools is essential for navigating when GPS technology is unreliable.
- Maps provide a broader overview of the area and can help in orienting oneself even without a GPS signal.
Compass Skills
- Basic compass skills, such as understanding cardinal directions, taking bearings, and triangulating positions, are valuable for navigating when GPS devices are unavailable.
- Learning how to use a compass in conjunction with a map can help travelers navigate accurately and efficiently in remote areas.
Mitigating Risks
Navigation Training
- Prioritize acquiring navigation skills through courses, workshops, or self-study to enhance your ability to navigate confidently in diverse environments.
- Practice using maps and compasses in familiar terrain before venturing into remote areas to build proficiency.
Pre-Trip Planning
- Plan your route using a combination of GPS technology, maps, and local knowledge to create a comprehensive navigation strategy.
- Identify key landmarks, waypoints, and alternative routes in case of GPS failure or navigation challenges.
Emergency Preparedness
- Carry backup batteries, paper maps, a reliable compass, and a knowledge of basic navigation techniques as part of your emergency kit.
- Communicate your travel plans with a trusted contact and establish check-in protocols to ensure your safety in case of navigation difficulties.
Navigating in remote areas without cellular coverage requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond relying solely on GPS technology. By acknowledging the limitations of GPS navigation and prioritizing backup navigation methods, such as traditional tools and skills, travelers can mitigate the risks associated with a lack of navigation skills. Building competence in map reading, compass use, and route planning enhances self-sufficiency and preparedness for navigating successfully in challenging environments where technology may falter.
2. Insufficient Trip Planning
Risks of Inadequate Trip Planning
Fuel Shortages
- Failing to plan for fuel stops and accurately estimate fuel consumption can result in running out of gas in remote areas with limited access to refueling stations.
- Being stranded without fuel can leave travelers stranded and vulnerable to harsh environmental conditions.
Water Scarcity
- Overlooking water sources and not carrying an adequate supply of water can lead to dehydration, especially in arid or desert regions where potable water may be scarce.
- Dehydration can compromise physical performance, cognitive function, and overall well-being, posing a significant health risk.
Lack of Emergency Supplies
- Neglecting to pack essential emergency supplies, such as first aid kits, tools, spare parts, and communication devices, can leave travelers ill-prepared to handle unexpected situations or emergencies.
- In remote areas, where help may be hours or days away, having the necessary supplies can make a critical difference in survival and safety.
Importance of Comprehensive Trip Planning
Route Assessment
- Conduct thorough research on the planned route, including road conditions, terrain challenges, elevation changes, and potential obstacles that may affect travel time and resource consumption.
- Identify fuel stations, water sources, rest areas, and emergency services along the route to ensure a well-prepared journey.
Resource Management
- Calculate fuel requirements based on distance, terrain, and vehicle efficiency to determine the necessary fuel stops and carry extra fuel reserves if needed.
- Pack an ample supply of potable water for drinking, cooking, and hygiene, considering the duration of the trip and the availability of water sources en route.
Emergency Preparedness
- Create a comprehensive emergency kit that includes first aid supplies, tools for vehicle repairs, spare tires, communication devices (e.g., satellite phone, emergency beacon), and extra food and water rations.
- Familiarize yourself with basic first aid procedures, vehicle maintenance tasks, and emergency protocols to respond effectively to unforeseen circumstances.
Mitigating Risks Through Planning
Checklists and Inventories
- Develop checklists for trip essentials, including fuel, water, food, emergency supplies, and vehicle maintenance tools, to ensure nothing crucial is overlooked.
- Conduct inventory checks before departure and restock supplies as needed to maintain readiness throughout the journey.
Contingency Planning
- Anticipate potential challenges, such as detours, road closures, or adverse weather conditions, and have contingency plans in place to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Stay flexible and responsive to unexpected events by having backup routes, alternative fuel sources, and communication strategies ready.
Insufficient trip planning can lead to critical shortages of fuel, water, and emergency supplies in remote overlanding expeditions, jeopardizing the safety and well-being of travelers. By conducting thorough route assessments, managing resources effectively, and prioritizing emergency preparedness, overlanders can mitigate risks and enhance their resilience in challenging environments. Comprehensive trip planning, coupled with proactive measures and contingency strategies, ensures a safer and more enjoyable overlanding experience in remote areas where access to essential resources may be limited.
3. Overestimating Vehicle Capability
Risks of Overestimating Vehicle Capability
Mechanical Failures
- Pushing a vehicle beyond its capabilities on challenging off-road routes can lead to mechanical breakdowns, such as engine overheating, transmission damage, or suspension failures.
- In remote areas without immediate access to repair facilities, vehicle breakdowns can result in being stranded and requiring costly recovery assistance.
Getting Stuck
- Attempting off-road routes that exceed the vehicle's traction, ground clearance, or maneuverability can result in getting stuck in mud, sand, or rocky terrain.
- Being immobilized in a remote location without the necessary recovery equipment or assistance can pose safety risks and delay the journey significantly.
Damage to Vehicle
- Subjecting the vehicle to extreme off-road conditions without proper preparation can lead to damage to the body, undercarriage, tires, and other components.
- Vehicle damage not only compromises safety and performance but also incurs repair costs and potential delays in the expedition.
Importance of Proper Vehicle Preparation
Vehicle Inspection
- Conduct a thorough pre-trip inspection of the vehicle, checking essential components such as tires, brakes, suspension, fluids, and lights to ensure they are in optimal condition for off-road travel.
- Address any maintenance issues or repairs before embarking on the journey to prevent breakdowns or malfunctions during the expedition.
Off-Road Modifications
- Equip the vehicle with appropriate off-road accessories, such as all-terrain tires, skid plates, lift kits, recovery gear (e.g., tow straps, winch), and protective equipment to enhance its capability in challenging terrain.
- Consider upgrades like differential locks, rock sliders, and upgraded suspension systems to improve off-road performance and durability.
Driver Training
- Develop off-road driving skills through training courses, workshops, or guided experiences to enhance your ability to navigate difficult terrain safely and effectively.
- Practice techniques such as proper tire inflation, throttle control, line selection, and recovery procedures to mitigate the risks of getting stuck or causing vehicle damage.
Mitigating Risks Through Vehicle Preparation
Weight Management
- Avoid overloading the vehicle with excessive gear and supplies, as added weight can strain the suspension, reduce fuel efficiency, and impact off-road performance.
- Pack essentials efficiently and prioritize lightweight, multi-purpose items to optimize the vehicle's handling and maneuverability.
Route Assessment
- Evaluate the difficulty level of off-road routes based on your vehicle's capabilities, ground clearance, approach/departure angles, and four-wheel-drive system.
- Choose routes that align with your vehicle's strengths and limitations to minimize the risks of mechanical failures or getting stuck.
Overestimating a vehicle's capability and attempting challenging off-road routes without proper preparation can lead to breakdowns, getting stuck, and vehicle damage in remote overlanding expeditions. By conducting thorough vehicle inspections, making necessary modifications, and acquiring off-road driving skills, travelers can mitigate risks and enhance their vehicle's performance in demanding terrain. Proper vehicle preparation, combined with prudent route selection and driver training, ensures a safer and more enjoyable overlanding experience in remote areas where self-reliance and vehicle resilience are paramount.
4. Not Carrying Adequate Supplies
Risks of Not Carrying Adequate Supplies
Dehydration and Malnutrition
- Running out of water and food supplies can lead to dehydration, fatigue, and impaired cognitive function, compromising your ability to navigate, make decisions, and respond to emergencies effectively.
- Inadequate hydration and nutrition can impact physical performance, increase the risk of heat-related illnesses, and jeopardize overall well-being during the expedition.
Exposure to Harsh Conditions
- Insufficient shelter, clothing, and bedding supplies can leave travelers vulnerable to extreme weather conditions, such as temperature fluctuations, strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Exposure to harsh environmental elements without proper gear can result in discomfort, hypothermia, heatstroke, or other weather-related health issues.
Emergency Situations
- Lacking essential emergency supplies, such as first aid kits, communication devices, tools, and spare parts, can hinder your ability to address medical emergencies, vehicle breakdowns, or unforeseen challenges.
- In remote areas with limited access to assistance, being ill-equipped for emergencies can escalate risks and delay necessary interventions.
Importance of Comprehensive Supply Management
Water and Food Reserves
- Calculate the amount of water needed for hydration, cooking, and hygiene based on the duration of the trip, weather conditions, and physical exertion.
- Pack non-perishable, high-energy foods that require minimal preparation and provide essential nutrients to sustain energy levels and mental acuity.
Shelter and Clothing
- Carry adequate shelter options, such as tents, tarps, or emergency blankets, to protect against inclement weather and provide a safe resting place.
- Dress in layers and pack weather-appropriate clothing, including moisture-wicking fabrics, insulating layers, waterproof outerwear, and sturdy footwear for varied conditions.
Emergency Supplies
- Assemble a comprehensive emergency kit that includes first aid supplies, medications, fire-starting tools, signaling devices, navigation aids, spare batteries, and a reliable communication device.
- Familiarize yourself with the contents of the emergency kit and how to use them effectively in different scenarios to respond promptly to emergencies.
Mitigating Risks Through Supply Management
Inventory Checklist
- Create a detailed inventory checklist of essential supplies, including water, food, shelter, clothing, emergency gear, and vehicle maintenance items, to ensure nothing vital is overlooked.
- Conduct regular inventory checks before and during the trip to monitor supply levels, replenish as needed, and maintain readiness for unexpected situations.
Resource Conservation
- Practice resource conservation strategies, such as rationing water and food, minimizing waste, and using supplies judiciously to extend their availability throughout the journey.
- Prioritize hydration, nutrition, and rest to maintain physical and mental resilience, especially in challenging or prolonged overlanding expeditions.
Not carrying adequate supplies, including water, food, shelter, and emergency gear, can pose significant risks to safety and well-being during remote overlanding adventures. By prioritizing comprehensive supply management, travelers can mitigate the risks of dehydration, exposure, and emergency situations, ensuring a more secure and enjoyable expedition experience. Proper planning, inventory checks, resource conservation, and emergency preparedness play a crucial role in safeguarding against potential supply shortages and enhancing self-sufficiency in remote environments where access to stores and assistance may be limited.
5. Neglecting Vehicle Maintenance
Risks of Neglecting Vehicle Maintenance
Mechanical Breakdowns
- Failing to conduct regular maintenance checks, such as inspecting fluid levels, tire condition, brakes, belts, and hoses, can increase the risk of mechanical failures while on the road.
- Vehicle components that are not properly maintained may be prone to malfunctions, leading to breakdowns in remote areas where immediate assistance is not readily available.
Reduced Reliability
- Neglected maintenance can compromise the overall reliability and performance of the vehicle, affecting its ability to navigate challenging terrain, withstand off-road conditions, and sustain long-distance travel.
- Unaddressed issues, such as engine overheating, transmission problems, or electrical faults, can escalate into more severe problems during the expedition.
Safety Concerns
- Vehicle maintenance lapses can pose safety hazards to both the occupants and other road users, as faulty brakes, worn tires, or malfunctioning lights increase the risk of accidents, especially in remote and rugged environments.
- Ensuring the vehicle is in optimal condition through regular maintenance checks is essential for mitigating safety risks and ensuring a secure overlanding experience.
Importance of Regular Vehicle Maintenance
Pre-Trip Inspection
- Conduct a comprehensive pre-trip inspection of the vehicle, including checking fluid levels (oil, coolant, brake fluid), tire pressure and tread depth, battery condition, lights, brakes, and suspension components.
- Address any maintenance issues, leaks, unusual noises, or warning lights before embarking on the journey to prevent potential breakdowns or performance issues.
Scheduled Maintenance
- Adhere to the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule for routine servicing, oil changes, filter replacements, and other scheduled maintenance tasks to keep the vehicle in optimal condition.
- Follow maintenance guidelines specific to off-road driving, such as cleaning air filters, greasing suspension components, and inspecting undercarriage protection.
Emergency Repair Kit
- Pack a basic emergency repair kit with essential tools, spare parts, fluids, and tire repair equipment to address minor mechanical issues or roadside repairs during the expedition.
- Familiarize yourself with basic vehicle repair procedures, such as changing a tire, jump-starting the battery, or replacing a fuse, to handle common roadside emergencies.
Mitigating Risks Through Vehicle Maintenance
Maintenance Records
- Keep detailed records of vehicle maintenance, repairs, and service history to track maintenance intervals, identify recurring issues, and ensure timely upkeep of critical components.
- Document maintenance tasks performed before each trip, including the date, mileage, and details of inspections or repairs conducted.
Proactive Approach
- Adopt a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance by addressing minor issues promptly, monitoring fluid levels regularly, and listening for unusual sounds or vibrations that may indicate underlying problems.
- Prioritize preventive maintenance to avoid costly repairs, unexpected breakdowns, and safety hazards while on the road.
Neglecting vehicle maintenance before embarking on a remote overlanding trip can lead to mechanical failures, reduced reliability, and safety concerns that jeopardize the success and safety of the expedition. By prioritizing regular maintenance checks, pre-trip inspections, scheduled servicing, and emergency repair preparedness, travelers can mitigate the risks associated with inadequate vehicle upkeep and enhance the overall reliability of their vehicle in challenging off-road environments. Proper maintenance practices, proactive monitoring, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines contribute to a safer, more reliable overlanding experience where vehicle performance and occupant safety are paramount.
6. Ignoring Weather Conditions
Risks of Ignoring Weather Conditions
Exposure to Extreme Temperatures
- Failing to monitor weather forecasts and prepare for temperature fluctuations can expose travelers to extreme heat or cold, leading to heat exhaustion, hypothermia, or frostbite.
- In remote areas with limited shelter options, inadequate clothing, or improper gear, exposure to extreme temperatures can pose significant health risks.
Severe Weather Events
- Disregarding the potential for storms, high winds, lightning, or flash floods in remote areas can leave travelers vulnerable to sudden weather changes and natural disasters.
- Being caught unprepared in severe weather conditions can jeopardize safety, damage equipment, and hinder travel progress, especially in rugged terrain.
Navigational Challenges
- Ignoring weather conditions that affect visibility, such as fog, snow, or heavy rain, can impede navigation, increase the risk of getting lost, and hinder communication with others.
- Limited visibility and adverse weather conditions can complicate route finding, increase the likelihood of accidents, and delay the journey significantly.
Importance of Weather Awareness
Weather Monitoring
- Stay informed about current and forecasted weather conditions in the region where you plan to overland, including temperature trends, precipitation chances, wind speeds, and potential weather hazards.
- Use reliable weather forecasting sources, such as weather radio, satellite communication devices, or offline weather apps, to track weather patterns and make informed decisions.
Preparation for Extreme Conditions
- Pack appropriate clothing layers, including moisture-wicking base layers, insulating mid-layers, waterproof outerwear, and protective gear for varying weather conditions.
- Carry emergency shelter options, such as tents, tarps, or bivvy sacks, to seek refuge from inclement weather and ensure a safe resting place in adverse conditions.
Adaptation and Contingency Planning
- Develop contingency plans for adverse weather scenarios, such as route diversions, alternative camping sites, or emergency shelters, to respond effectively to changing weather conditions.
- Stay flexible and adaptable in your travel itinerary, adjusting plans as needed based on weather updates, local advice, and safety considerations.
Mitigating Risks Through Weather Preparedness
Safety Briefings
- Conduct pre-trip safety briefings with all travelers to discuss weather risks, emergency protocols, shelter options, and communication plans in case of severe weather events.
- Establish clear communication channels and emergency signals to coordinate responses to weather-related emergencies and ensure the safety of all expedition members.
Risk Assessment
- Assess the potential impact of weather conditions on your route, camping locations, and outdoor activities, considering factors such as elevation, terrain exposure, and proximity to water bodies.
- Monitor weather updates regularly during the trip and adjust plans proactively to mitigate risks, prioritize safety, and optimize the overlanding experience.
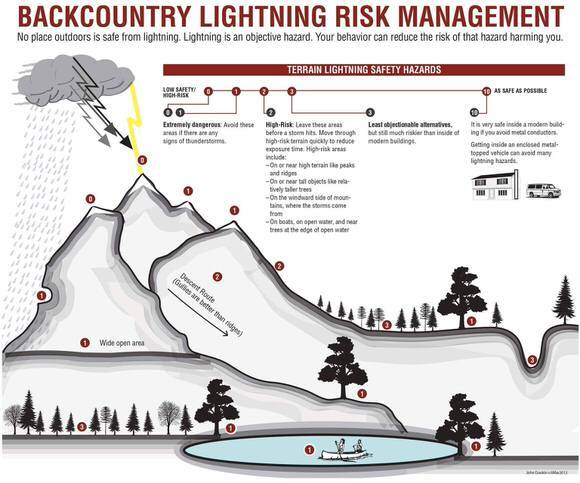
Ignoring weather conditions in remote overlanding expeditions can lead to exposure risks, safety hazards, and navigational challenges that compromise the well-being and success of the journey. By prioritizing weather awareness, preparation for extreme conditions, and adaptation strategies, travelers can mitigate the risks associated with unpredictable weather patterns and ensure a safer, more resilient overlanding experience in remote areas. Proactive monitoring, contingency planning, and effective communication contribute to weather readiness, risk mitigation, and enhanced safety measures that support a successful and enjoyable overlanding adventure.
7. Lack of Communication Plan
Risks of Lack of Communication Plan
Isolation in Emergencies
- Without a reliable communication plan, travelers may find themselves isolated in case of emergencies, accidents, or medical crises, unable to seek timely assistance or alert authorities.
- Delayed communication with emergency services or support networks can exacerbate the severity of the situation and hinder the prompt response required for effective rescue operations.
Lost Contact with Travel Companions
- In the absence of a communication plan, travelers may lose contact with their companions or support team, leading to confusion, disorientation, and challenges in coordinating responses to unexpected events.
- Communication breakdowns can impede decision-making, increase anxiety levels, and compromise the safety and well-being of all expedition members.
Inability to Request Help
- Without a means to call for help or signal distress, travelers facing mechanical breakdowns, medical emergencies, or other critical incidents may struggle to request assistance, leading to prolonged exposure to risks and uncertainties.
- A lack of communication options limits the ability to convey vital information, seek guidance, or coordinate rescue efforts in challenging or remote environments.
Importance of a Communication Plan
Emergency Contact Information
- Compile a list of emergency contact numbers, including local emergency services, park rangers, towing services, and trusted contacts who can assist in case of emergencies.
- Share this information with all expedition members and ensure everyone knows how to access and use communication devices effectively.
Communication Devices
- Carry reliable communication devices, such as satellite phones or emergency communications devices (like inReach or SPoT devices,) emergency beacons (EPIRBs/PLBs),and/or two-way radios, that can transmit distress signals and GPS coordinates in remote areas without cellular coverage. [NOTE: My preferred emergency communications device is a Garmin inReach, in particular a Garmin inReach Mini 2.]
- Test communication devices before the trip, familiarize yourself with their operation, and ensure they are fully charged and in working condition throughout the expedition.
Check-In Protocols
- Establish regular check-in protocols with a designated contact person or monitoring service to provide updates on your location, status, and well-being at specified intervals during the trip.
- Agree on emergency signals, distress codes, or communication protocols to convey urgent messages and trigger assistance when needed.
Mitigating Risks Through Communication Planning
Communication Drills
- Practice using communication devices, sending distress signals, and relaying emergency information through role-playing scenarios or simulated emergencies to enhance response readiness.
- Familiarize all expedition members with communication protocols, emergency procedures, and the location of communication devices in the event of an emergency.
Redundant Communication Channels
- Implement redundant communication channels, such as multiple devices, backup batteries, signal mirrors, whistle, or flares, to ensure alternative means of signaling for help in case primary devices fail.
- Diversify communication options to include both short-range (radios) and long-range (satellite phones) devices for comprehensive coverage in remote areas with varying terrain and conditions.
A lack of communication plan in remote overlanding expeditions can impede emergency response, jeopardize safety, and hinder coordination efforts in critical situations. By prioritizing the development of a comprehensive communication plan, including emergency contact information, reliable communication devices, check-in protocols, and communication drills, travelers can mitigate the risks associated with isolation, lost contact, and inability to request help. Effective communication planning, proactive testing, and clear protocols enhance the safety, resilience, and preparedness of overlanders in remote environments where access to assistance may be limited.
8. Solo Travel Without Backup
Risks of Solo Travel Without Backup
Limited Assistance
- Venturing into remote areas alone reduces the availability of immediate assistance in case of vehicle breakdowns, medical emergencies, or other unforeseen situations.
- Being solo means there is no backup support to help with navigation, vehicle recovery, first aid, or decision-making during challenging circumstances.
Increased Vulnerability
- Solo travelers are more vulnerable to risks such as getting stuck in difficult terrain, encountering wildlife, facing adverse weather conditions, or experiencing mechanical failures without the support of a companion.
- In the event of an emergency, being alone can heighten feelings of isolation, stress, and uncertainty, amplifying the impact of the situation on mental and emotional well-being.
Limited Resources
- Traveling solo without backup means there are fewer resources available for problem-solving, vehicle recovery, gear maintenance, and other essential tasks that may require additional hands or expertise.
- Lack of backup support may limit the ability to address challenges effectively, leading to prolonged delays, increased risks, and potential escalation of emergencies.
Importance of Backup Support
Companion or Convoy
- Consider traveling with a companion or joining a convoy of fellow overlanders to provide mutual support, shared resources, and backup assistance in case of emergencies or challenges.
- Having a travel companion enhances safety, communication, decision-making, and overall resilience during the expedition, particularly in remote and unpredictable environments.
Vehicle Recovery Gear
- Equip your vehicle with essential recovery gear, such as traction boards, tow straps, winches, and recovery tracks, to enhance self-recovery capabilities in case of getting stuck or encountering obstacles.
- Familiarize yourself with proper recovery techniques and safety protocols to effectively use the equipment and navigate challenging terrain independently if needed.
Emergency Communication
- Carry reliable communication devices, such as satellite phones, emergency beacons, or two-way radios, to signal for help, transmit distress signals, and communicate with emergency services or support networks in case of emergencies.
- Establish check-in protocols with a trusted contact or monitoring service to maintain regular communication and provide updates on your location and well-being during solo expeditions.
Mitigating Risks of Solo Travel Without Backup
Safety Precautions
- Prioritize safety precautions, such as wearing appropriate gear, carrying emergency supplies, informing others of your travel plans, and adhering to established safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with solo travel.
- Maintain situational awareness, practice risk assessment, and exercise caution in decision-making to enhance personal safety and preparedness during solo overlanding expeditions.
Self-Sufficiency
- Enhance self-sufficiency by acquiring essential skills, such as navigation, vehicle maintenance, first aid, and emergency response, to handle a range of situations independently and effectively while traveling solo.
- Develop a comprehensive emergency plan, including contingency measures, alternative routes, and self-rescue strategies, to address potential challenges and ensure resilience in remote environments.
Solo travel without backup in remote overlanding expeditions presents unique challenges and considerations that impact safety, support, and resource availability. By recognizing the risks associated with solo travel, prioritizing backup support, equipping the vehicle with recovery gear, establishing emergency communication protocols, and enhancing self-sufficiency through skills development and preparedness, solo overlanders can mitigate risks, enhance safety, and optimize their resilience in remote environments. Thoughtful planning, proactive measures, and a cautious approach contribute to a safer and more rewarding solo overlanding experience, where self-reliance, adaptability, and preparedness are essential for navigating the uncertainties of remote travel.
9. Disregarding Local Regulation
Risks of Disregarding Local Regulations
Legal Consequences
- Ignoring local regulations on camping, off-roading, land use, and environmental protection can result in fines, citations, legal penalties, and potential restrictions on future access to public lands.
- Violating regulations related to wilderness areas, protected habitats, or cultural sites can lead to legal repercussions, damage to natural resources, and negative impacts on local communities.
Environmental Damage
- Disregarding off-road restrictions, trail closures, or camping bans can contribute to soil erosion, habitat destruction, vegetation damage, and disturbance of wildlife populations in fragile ecosystems.
- Unregulated off-roading practices, improper waste disposal, and disregard for Leave No Trace principles can harm the environment, degrade natural landscapes, and compromise biodiversity conservation efforts.
Community Relations
- Ignoring local regulations can strain relationships with residents, land managers, and other outdoor enthusiasts who value responsible land stewardship, sustainable recreation practices, and adherence to established rules.
- Disrespecting local customs, cultural heritage sites, or traditional territories can lead to community backlash, social conflicts, and a negative reputation for overlanders in the area.
Importance of Compliance with Local Regulations
Research and Education
- Conduct thorough research on local regulations, land management policies, camping restrictions, off-road designations, and environmental guidelines before embarking on an overlanding trip.
- Educate yourself on the specific rules and regulations governing the area you plan to visit, including permit requirements, camping zones, fire restrictions, waste disposal guidelines, and wildlife protection measures.
Responsible Recreation
- Practice responsible recreation by following designated trails, respecting trail closures, staying on established roads, and avoiding off-road driving in sensitive habitats, wetlands, or protected areas.
- Adhere to Leave No Trace principles, pack out all trash, minimize impact on natural resources, and leave the environment as you found it to preserve the integrity of the landscape for future generations.
Engagement with Authorities
- Establish positive relationships with local land managers, park rangers, conservation officers, and community stakeholders by seeking information, obtaining permits, and respecting their expertise in managing public lands.
- Collaborate with authorities to understand conservation goals, recreational opportunities, and cultural sensitivities in the area, and contribute to sustainable land use practices through responsible overlanding behavior.
Mitigating Risks Through Compliance
Regulatory Compliance
- Familiarize yourself with the rules and regulations specific to the area you are visiting, including camping restrictions, fire bans, wildlife protection measures, and off-road vehicle requirements, to ensure compliance with local laws.
- Obtain necessary permits, licenses, or passes for camping, off-roading, or recreational activities in designated areas and follow all permit conditions to avoid legal issues and support conservation efforts.
Community Engagement
- Engage with local communities, land managers, and conservation organizations to learn about their priorities, concerns, and initiatives related to land stewardship, environmental protection, and sustainable recreation practices.
- Participate in volunteer programs, educational events, or community outreach activities to support conservation efforts, build positive relationships, and contribute to the responsible use of public lands.
Disregarding local regulations on camping, off-roading, and land use in remote overlanding expeditions can lead to legal consequences, environmental damage, and community conflicts that undermine the integrity of outdoor recreation and conservation efforts. By prioritizing compliance with local regulations, conducting thorough research, practicing responsible recreation, engaging with authorities and communities, and advocating for sustainable land use practices, overlanders can mitigate risks, foster positive relationships, and contribute to the preservation of natural resources and cultural heritage in remote areas. Responsible overlanding behavior, regulatory compliance, and environmental stewardship are essential for promoting ethical and sustainable outdoor recreation practices that respect local regulations, protect the environment, and support the long-term health of public lands for future generations.
10. Overlooking Personal Safety
Risks of Overlooking Personal Safety
Medical Emergencies
- Neglecting first aid training and emergency response knowledge can leave travelers ill-equipped to handle medical emergencies, injuries, or health crises that may occur during the expedition.
- In remote environments without immediate access to medical facilities, lacking basic first aid skills can delay critical interventions and worsen the outcomes of medical emergencies.
Safety Hazards
- Ignoring safety precautions, such as vehicle maintenance, navigation skills, and wildlife awareness, can increase the risk of accidents, mechanical failures, navigation errors, and encounters with hazardous wildlife in remote areas.
- Inadequate safety measures can lead to injuries, vehicle breakdowns, lost or disoriented situations, and exposure to environmental hazards that compromise personal safety and well-being.
Wildlife Encounters
- Disregarding wildlife awareness and proper behavior around animals can result in dangerous encounters, conflicts with wildlife, or unintentional disturbances to natural habitats in remote wilderness areas.
- Lack of knowledge about wildlife behavior, habitat protection, and appropriate responses to encounters can escalate risks, provoke wildlife aggression, and pose threats to both humans and animals.
Importance of Personal Safety Precautions
First Aid Training
- Acquire basic first aid training, CPR certification, and wilderness first aid skills to respond effectively to medical emergencies, injuries, and health issues while overlanding in remote areas.
- Carry a well-equipped first aid kit, medications, and emergency supplies to address common injuries, illnesses, and medical conditions encountered during outdoor adventures.
Emergency Response Knowledge
- Develop emergency response knowledge, including navigation skills, communication protocols, distress signals, and survival techniques, to handle unforeseen situations, lost scenarios, or distress calls in remote environments.
- Create an emergency plan, share it with travel companions or trusted contacts, and practice emergency drills to enhance preparedness and response capabilities during overlanding expeditions.
Wildlife Awareness
- Educate yourself about local wildlife species, their habitats, behaviors, and conservation status to minimize human-wildlife conflicts, respect natural ecosystems, and promote responsible wildlife viewing practices.
- Follow wildlife viewing guidelines, maintain a safe distance from animals, avoid feeding wildlife, and secure food and waste to prevent attracting wildlife to campsites and reduce the risk of negative interactions.
Mitigating Risks Through Personal Safety Measures
Safety Briefings
- Conduct pre-trip safety briefings with all expedition members to review safety protocols, emergency procedures, first aid response, wildlife awareness, and communication strategies for ensuring personal safety during the journey.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities, assign safety tasks, and communicate emergency contact information to facilitate coordinated responses to potential risks and emergencies.
Continual Learning
- Stay informed about safety best practices, outdoor survival skills, and wilderness safety tips through training courses, workshops, online resources, and outdoor education programs to enhance personal safety knowledge and preparedness.
- Engage in ongoing learning opportunities, seek mentorship from experienced outdoors enthusiasts, and participate in skill-building activities to improve personal safety skills and confidence in remote environments.
Overlooking personal safety precautions, such as first aid training, emergency response knowledge, and wildlife awareness, can expose overlanders to significant risks, vulnerabilities, and challenges in remote environments. By prioritizing personal safety measures, acquiring essential skills, developing emergency response knowledge, and practicing wildlife awareness, travelers can mitigate risks, enhance preparedness, and promote a safer overlanding experience in wilderness areas. Responsible safety practices, continual learning, proactive risk management, and effective communication contribute to personal well-being, resilience, and enjoyment of outdoor adventures while fostering a culture of safety, respect for nature, and responsible recreation in remote overlanding expeditions.
To avoid these common mistakes when overlanding in remote areas, it's crucial to prioritize thorough trip planning, vehicle maintenance, emergency preparedness, and safety precautions. Always be self-sufficient, informed, and mindful of your surroundings to ensure a safe and enjoyable overlanding experience in remote areas.
Epilogue: Check out my Amazon affiliate store for gear I have personally used while overlanding and fully recommend: https://www.amazon.com/shop/azarinelli Let me know if there are any items in my lists you would like me to write a comprehensive review about, or if you would like me to elaborate in more detail on any of the tips I give above!


















